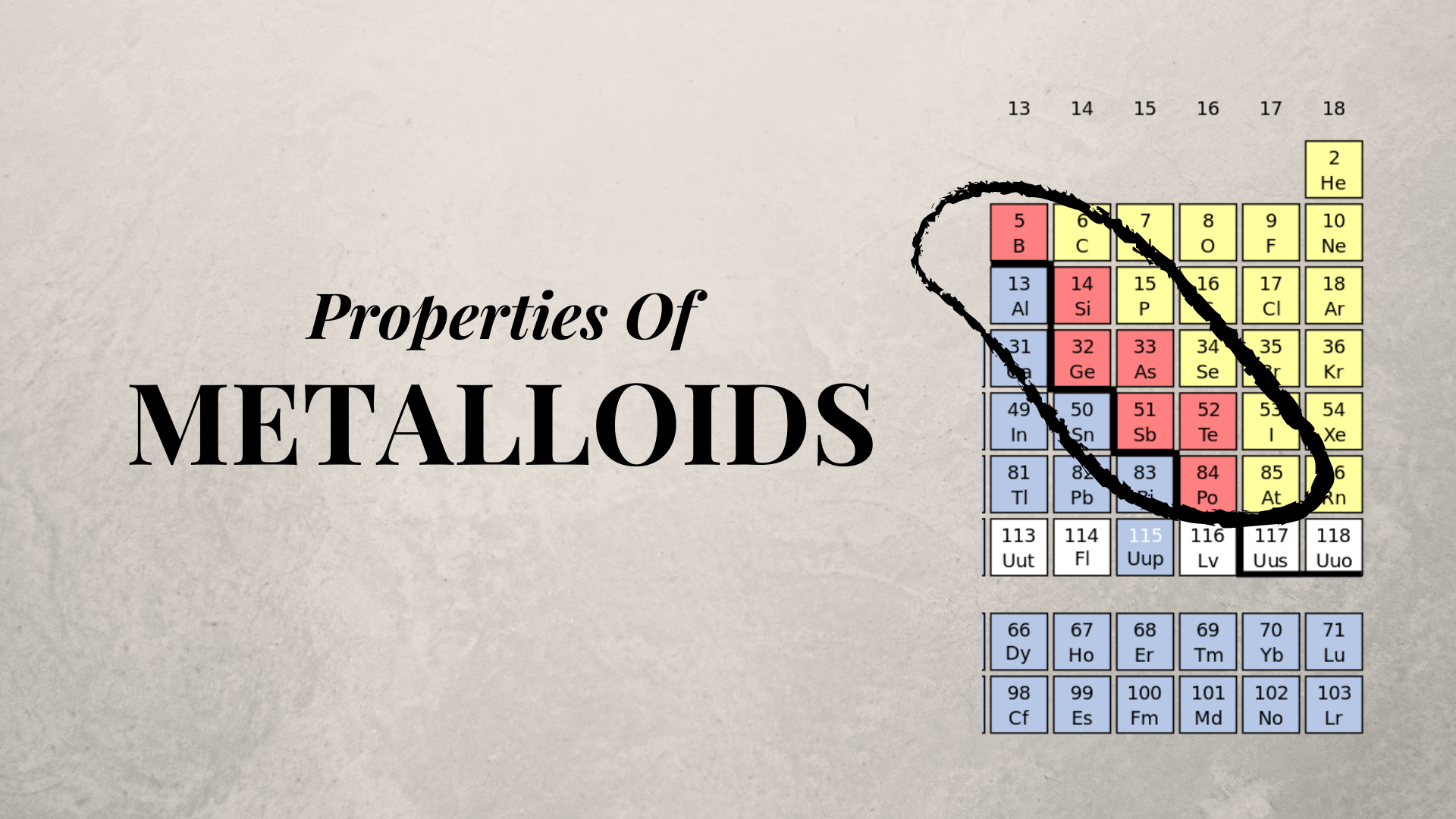
Metalloids Key Reactions . Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table. Web structures of the metalloids. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium.
from sciencetrends.com
Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Web structures of the metalloids. Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids.
4 Properties Of Metalloids Science Trends
Metalloids Key Reactions Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having. Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table. Web structures of the metalloids. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids.
From www.thoughtco.com
Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids Worksheet Metalloids Key Reactions Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having. Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table. Web structures of the metalloids. Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From www.researchgate.net
Summary of the key reactions in the ODH and reoxidation halfcycles Metalloids Key Reactions Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Common. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From slideplayer.com
Chapter 4 Section 4 Nonmetals and metalloids ppt download Metalloids Key Reactions Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table. Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From dokumen.tips
(PPTX) Properties of Materials And Chemical Reactions. S1207 Metalloids Key Reactions Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Web structures of the metalloids. Web metalloid, in chemistry,. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Atoms and Atomic Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download Metalloids Key Reactions Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From www.difference101.com
Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids 5 Key Differences, Pros & Cons Metalloids Key Reactions Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having. Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Web structures of the metalloids. Where are the metalloids located on the. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From www.youtube.com
157 What is metalloids? Give the example. YouTube Metalloids Key Reactions Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having. Web structures of the metalloids. Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From sciencenotes.org
List of Metalloids or Semimetals Metalloids Key Reactions Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Web structures. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT 9E Reactions of metals and their compounds PowerPoint Metalloids Key Reactions Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having. Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids.. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From www.difference101.com
Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids 5 Key Differences, Pros & Cons Metalloids Key Reactions Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table. Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Web covalent bonding is the key. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT 7.6 Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids PowerPoint Presentation Metalloids Key Reactions Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Common. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From newtondesk.com
Metalloids (Periodic Table) Properties, Uses, & Facts Metalloids Key Reactions Web structures of the metalloids. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having. Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Where are the. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From www.periodictableprintable.com
Metals Nonmetals And Metalloids Located On Periodic Table 2024 Metalloids Key Reactions In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having. Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. Where are the metalloids located on the periodic. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From sciencetrends.com
4 Properties Of Metalloids Science Trends Metalloids Key Reactions Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Where are the. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From derekcarrsavvy-chemist.blogspot.com
savvychemist GCSE OCR Gateway Chemistry C2.2 ac Metals and nonmetals Metalloids Key Reactions Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. Web structures of the metalloids. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone of modern electronics because of our ability. Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table. Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Web. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Periodic Table PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1587804 Metalloids Key Reactions Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table. Web structures of the metalloids. Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Web for example, silicon and. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Orbital Diagrams and Electron Configuration PowerPoint Metalloids Key Reactions In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Web structures of the metalloids. Web metalloid, in chemistry, an imprecise term used to describe a chemical element that forms a simple substance having. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors. Metalloids Key Reactions.
From www.difference101.com
Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids 5 Key Differences, Pros & Cons Metalloids Key Reactions In this regard, these elements resemble nonmetals in. Common metalloids include boron (b), silicon (si), germanium. Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table. Web covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Covalent bonding is the key to the crystal structures of the metalloids. Web for example, silicon and other semiconductors form the backbone. Metalloids Key Reactions.